Baby hiccups
SYMPTOMS
What Causes Baby Hiccups?
Newborns and infants, like adults, have a muscle called the "diaphragm" between the chest and abdominal cavities. It separates and protects the organs in these cavities.
When a baby feeds too quickly, swallows a lot of air, or is exposed to cold temperatures, the autonomic nerves are stimulated, causing the diaphragm to contract suddenly. This forces air from the stomach toward the throat, briefly closing the vocal cords and producing the classic "hic" sound.
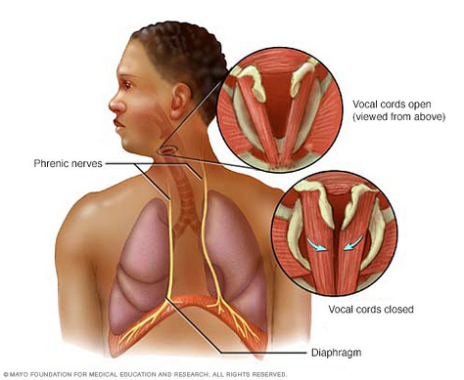
Babies often make this sound rhythmically after feeding, which is what we commonly refer to as hiccups.
Hiccups usually occur after eating or crying and are generally a normal physiological process. They do not cause pathological issues and typically resolve on their own as the baby matures, requiring no excessive intervention.
What Are Hiccups?
Hiccups, medically termed "singultus," are different from burping (belching).
Hiccups occur due to diaphragm spasms, causing sudden vocal cord closure and producing the characteristic "hic" sound.
TREATMENT
When Should You Burp Your Baby?
It is recommended to burp newborns and infants in the following three situations:
Baby becomes fussy during feeding: If the baby starts getting restless during feeding but clearly hasn't had enough, it might be due to trapped gas. Pause feeding and burp the baby.
Baby feeds too quickly: Rapid feeding and large gulps can lead to swallowing air.
Bottle feeding: Bottle-fed babies tend to swallow more air compared to breastfeeding, making burping more necessary.
What Can You Do When Your Baby Has Persistent Hiccups?
Generally, hiccups are normal for babies, and most experience them occasionally. Parents need not worry too much. As the baby grows and the diaphragm matures, hiccups will gradually decrease, usually without requiring intervention.
However, if parents wish to alleviate the baby's discomfort, they can try the following methods:
For young infants:
- Change feeding position + burping. If hiccups occur during feeding, adjust the baby's position and try burping. Resume feeding once the hiccups stop. If hiccups persist for 5–10 minutes, try feeding again—some babies stop hiccups while nursing.
- Use a pacifier. Sucking a pacifier may help relax the diaphragm and stop hiccups.
- Gently massage the baby's back. This can help calm the baby and relax the diaphragm.
For older babies:
- Try briefly holding their breath or performing the Valsalva maneuver (inhaling deeply, holding, then exhaling forcefully); sip cold water.
- Gargle with water, hold it briefly, then spit it out.
- Eat a small spoonful of sugar.
- Squat with knees bent to the chest, leaning forward.
Note: The effectiveness of these methods isn't guaranteed, but they are safe to try at home.
How to Burp a Baby with Hiccups?
Hand position:
Cup your hand slightly, keeping the palm hollow to avoid direct contact with the baby's back. Avoid a flat "high-five" position, as it may cause discomfort.
Burping frequency:
Aim for 50–60 pats per minute, ensuring the baby isn't uncomfortable.
Burping timing:
Burp immediately after feeding or during breaks. If the baby fusses or cries, pause to burp before resuming feeding. A burping session should last 3–5 minutes.
What Are the Burping Positions for Babies?
1. Over-the-shoulder burping:
Hold the baby upright against your shoulder, supporting their head and gently patting their back from bottom to top.
2. Sitting-on-lap burping:
Sit the baby on your lap, leaning them slightly forward, and support their chest and head while patting their back.
3. Airplane hold burping:
Lay the baby face-down on your forearm, with their head slightly elevated, and pat their back gently.
Key tip: Keep the baby's head higher than their stomach and support their neck to prevent wobbling.
If no burp occurs after a few minutes, continue feeding and try again later.
Should You Burp After Every Feeding?
It's advisable to burp after each feeding, but if the baby doesn't spit up or burps naturally when held upright, burping isn't mandatory.
Infants often spit up due to their horizontal stomach position and underdeveloped muscles. Burping helps release trapped air, reducing discomfort and spitting up. Once the baby starts eating solid foods, burping becomes less necessary.
Should You Burp After Night Feedings?
Observe the baby's comfort level:
- Breastfed babies: Side-lying nursing reduces air intake. If the baby sleeps comfortably without burping, it's unnecessary.
- Bottle-fed babies: More likely to swallow air, so burping can prevent nighttime fussiness and spit-up.
If the baby sleeps well without burping, it can be skipped as they grow older.
Seek medical help if hiccups persist beyond 48 hours or interfere with eating, sleeping, or breathing.
How to Prevent Baby Hiccups?
1. Proper feeding techniques:
- Bottle feeding: Use an appropriately sized nipple, hold the baby upright, and tilt the bottle slightly to avoid air intake.
- Breastfeeding: Ensure a deep latch to minimize air swallowing.
2. Calm feeding environment: Avoid distractions to prevent gulping air.
3. Proper formula mixing: Roll the bottle instead of shaking vigorously to reduce bubbles.
Feed before the baby becomes overly hungry or upset, and pause midway to burp if needed.
How to Prevent Frequent Hiccups?
- Avoid feeding during crying or extreme hunger. Feed when the baby is calm to prevent rapid air swallowing.
- Ensure proper latch during breastfeeding. Adjust if milk flow is too fast.
- Choose the right bottle nipple. Match the nipple size to the baby's age and keep the bottle angled to minimize air.
DIAGNOSIS
When should a baby's hiccups require a hospital visit?
Baby hiccups are usually physiological because the baby's diaphragm, including the autonomic nerves that regulate it, are not yet fully developed, making them prone to hiccups.
Temporary hiccups generally do not require treatment and will resolve on their own after some time.
Seek medical attention promptly if the following occurs:
-
The baby hiccups frequently, lasting more than 48 hours—this is called persistent hiccups; if hiccups last for over 2 months, it is termed intractable hiccups.
-
Severe hiccups that interfere with eating, sleeping, or breathing, accompanied by poor appetite, weight loss, or frequent vomiting, may indicate less common causes such as gastroesophageal reflux, pneumonia, adverse drug reactions, etc., and require immediate medical attention.
A doctor can help analyze the specific cause of the baby's hiccups and determine whether targeted treatment is needed, such as checking for neurological disorders, gastrointestinal diseases, thoracic or lung conditions, cardiovascular diseases, poisoning or metabolic abnormalities, medication effects, or psychological factors.
If any underlying conditions are suspected, active intervention and treatment may be necessary, after which the hiccups will naturally subside.
POTENTIAL DISEASES
What are the possible causes of baby hiccups?
Baby hiccups may be caused by the following reasons:
- Improper feeding: Such as eating too quickly, too eagerly, or too much, or incorrect feeding posture leading to swallowing large amounts of air;
- Emotional changes: Such as intense crying or excited laughter causing stimulation and swallowing air;
- Temperature changes: Such as sudden temperature changes or exposure to cold stimuli.
These factors can cause diaphragmatic spasms, leading to hiccups.
Why do babies frequently get hiccups?
Hiccups, medically known as singultus, are a very common phenomenon, especially in newborns. They are caused by the baby's diaphragm contracting intermittently.
The main reasons include the following:
- Physiological factors: Due to the immature development of the baby's autonomic nervous system, the diaphragm's movements are not well-coordinated. When slightly stimulated, the diaphragm suddenly contracts, causing rapid inhalation and producing the "hic" sound.
- Swallowing large amounts of air: Including improper bottle use, incorrect feeding posture, or feeding too quickly, all of which may cause the baby to swallow large amounts of air, stimulating the diaphragm and resulting in hiccups.
- Other factors: Overeating leading to excessive stomach distension, intestinal gas, consuming overly hot or irritating foods, drinking soda or other carbonated beverages, indigestion, gastroesophageal reflux, etc.